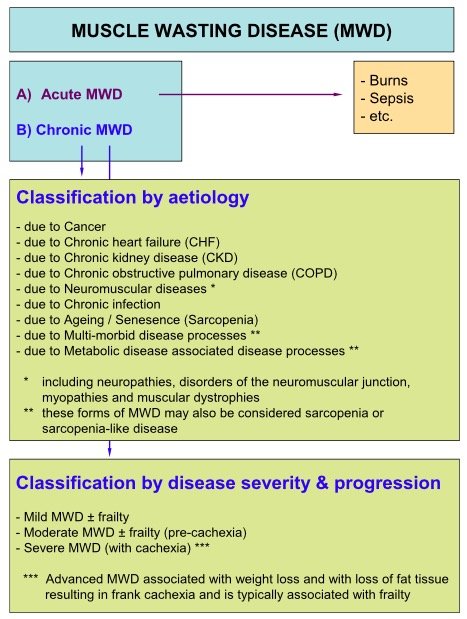
Muscle Wasting Disease (MWD) in Cachexia and Sarcopenia
Weight loss is the hallmark of any progressive acute or chronic disease state. In its extreme form, it involves a significant lean body mass (including skeletal muscle), and fat loss. Skeletal muscle provides a fundamental basis for human function, enabling locomotion and respiration. Muscle wasting is related to a poor quality of life and increased morbidity/ mortality.
Two common but distinct conditions characterized by a loss of skeletal muscle mass are sarcopenia and cachexia. Sarcopenia, cachexia, and anorexic disorders (protein-energy malnutrition) represent the major causes of muscle-wasting disorders.
It has been known for millennia that muscle and fat wasting leads to poor outcomes including deaths in chronic disease states.
It is usually accompanied by physical inactivity, decreased mobility, slow gait, and poor physical endurance which are also common features of the frailty syndrome.
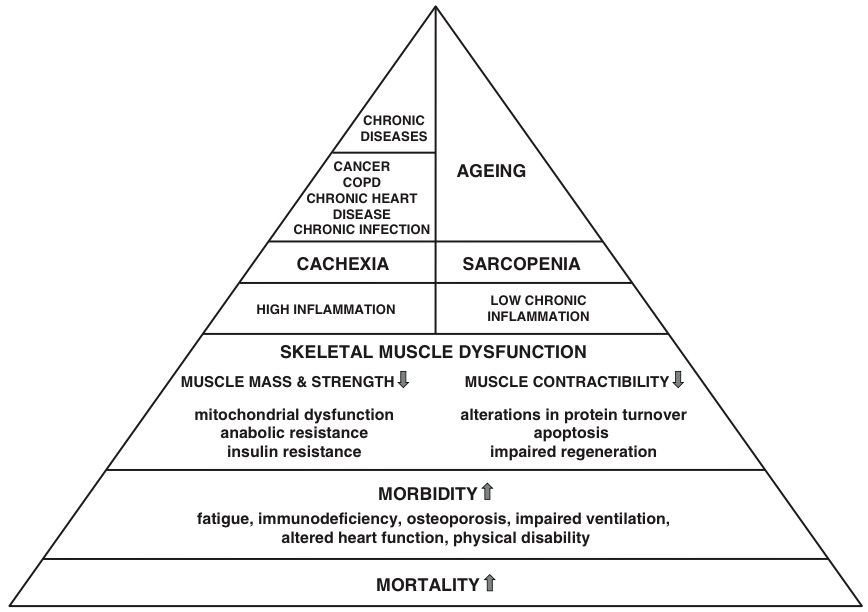
Both cachexia and sarcopenia are characterized by an important muscle dysfunction that leads to increased morbidity and mortality.
References
Kalantar-Zadeh K, Rhee C, Sim JJ, Stenvinkel P, Anker SD, Kovesdy CP. Why cachexia kills: examining the causality of poor outcomes in wasting conditions. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2013; 4: 89–94.
Evans WJ, Morley JE, Argilés J, Bales C, Baracos V, Guttridge D, et al. Cachexia: a new definition. Clin Nutr 2008; 27: 793–799.
Anker SD, Coats AJS, Morley JE, Rosano G, Bernabei R, Haehling S, et al. Muscle wasting disease: a proposal for a new disease classification. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2014; 5: 1–3.
Argiles JM, Busquets S, Stemmler B, López-Soriano FJ. Cachexia and sarcopenia: mechanisms and potential targets for intervention. Current Opinion in Pharmacology 2015; 22: 100–106.
Bowen TS, Schuler G, Adams V. Skeletal muscle wasting in cachexia and sarcopenia: molecular pathophysiology and impact of exercise training. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2015; 6: 197–207.


